Most of Earth is covered by ocean.
Oceans give us food and a place to play.
Oceans help keep the air temperature steady.
Lots of plants and animals live in the ocean.
On the ocean bed there are mountains, valleys and even volcanoes.
Earth - the watery planet
Nearly three quarters of the earth's surface is covered by water. About 97% of that water is ocean, or salt water, which is the marine biome.
The other 3% is freshwater, frozen in glaciers and icecaps, or in lakes, rivers or in the air.
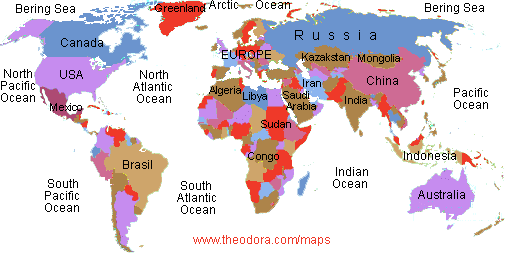
Sections of the ocean
Continents separate and divide the ocean into sections, which gives us five oceans. The largest is the Pacific Ocean, then the Atlantic Ocean and the Indian Ocean. Where the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans meet near the continent of Antarctica, the ocean is called the Antarctic or Southern Ocean. There is also the Arctic Ocean. Each ocean has smaller parts called seas, gulfs or bays. These are at the edges of oceans.
Ocean waves ©Getty
What the ocean gives us
The ocean provides us with food, energy and minerals. It allows us to swim, sail in boats, surf and other water activities. The ocean helps regulate the air temperature and supplies moisture for rainfall.
Under the ocean
The bottom of the ocean has high mountains, wide plains and deep valleys. There are even volcanoes on the ocean floor.
The Mariana Trench
Mostly the ocean is about 4000 metres deep, but is deeper in some places. The deepest known point is in the Mariana Trench, north of New Guinea. The Mariana Trench is stretches for about 2,500 km, and ranges in width from 70km to 338km. The deepest point of the Mariana Trench is called Vitjazdepth and is 11,035 metres deep. This is the deepest part of Earth that we know about.
Salty water
The salt in the oceans comes from rocks on land which gets washed down into the ocean. Rain falls on the land and the water filters through rocks and sand and collects minerals and salts as it makes its way into the ocean. About 90 percent of the salts in the ocean are sodium and chloride. Salts are also released by underwater volcanoes.
Sunlight reaching the ocean floor. ©Getty
Evaporation is a natural process that causes water to change from a liquid to a vapour, or gas. The sun evaporates water, which turns into vapour and becomes part of the air, leaving the salt behind. In hotter places, the rate of evaporation is greater. The amount of evaporation depends on the amount of water, so there is more evaporation from a big lake than from puddles on the land. Tropical rainforests are very moist areas because they get so much rain, so therefore there is a high evaporation rate.
Food from the ocean
Food provided by the ocean is fish, shellfish, and seaweed. Kelp, a kind of seaweed, provides algin, which is used as a thickening in ice cream, salad dressing and cosmetics. Fish farming, or aquaculture, is increasing in western countries. It has been practiced in Asian countries for hundreds of years. Fish farmers raise fish, shellfish and seaweeds in special ponds or along the seashore.
A marine mammal, a leopard seal. © Getty
Energy from the ocean
Oil and natural gas are the main energy resources provided by the ocean. They are found in the earth under the oceans.
Scientists are exploring ways to use the energy of waves to make electricity. A cleaner and renewable form of energy.
Marine animals
Many creatures live in the ocean, from tiny organisms like krill to the largest mammal ever, the blue whale. Many other creatures spend much of their time in or near the ocean, such as penguins and seals.
Sharks are the top predators in the ocean. ©Getty
It’s a good idea to get information from more than one source!
Read about the ocean, or marine, biome:
This website was sent to us by Stella, a student who thought it would be good to share on this page:
https://www.123filter.com/ac/oceanography-resource-guide-for-water-studies
Watch videos about oceans
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YWPtavQ2oRY
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UGm2Eg1Q8Lc