Eyes are like cameras.
They take pictures of what we are looking at.
They send a message to the brain.
The brain tells us what we are seeing.
How the eye works
The eyes work like cameras. Light passes through the pupil to the lens in your eye. The lens focuses the light onto the retina to make a picture of what you are looking at.
The retina turns the picture into an electric message which travels along a nerve called the optic nerve. The optic nerve carries the message to the brain and the brain tells you what you are seeing.
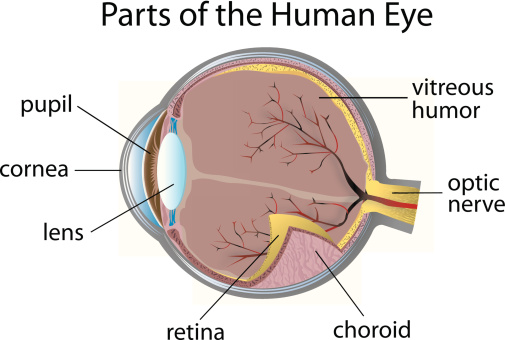
The parts of the eye
The cornea (say cor-nee-uh) is the clear skin that covers the eye.
The iris (say eye-ris) is the coloured part of the eye. It controls the amount of light that enters the eye. The iris can be brown, blue, green and other colours in different people.
The pupil (say pew-pil) this is the black dot in the coloured iris. It is a hole in the eye and it changes shape. It gets bigger in dull light, and smaller when the light is bright.
The lens focuses light onto the retina, changing shape to make the picture as clear as possible.
The retina is where the picture is 'screened'. On the retina the picture is upside down! (the brain will turn it the right way up later) Different cells (parts) in the retina called rods and cones can see colours and black and white. The rods see black and white, while the cones see colour. They turn the picture into electrical signals.
The optic nerve takes the electrical signals to the brain and the brain turns the picture right way up and tells us what we are seeing.
The vitreous humor (say vit-ree-us) is like a jelly. It keeps the eyeball in shape.
The choroid (say cor-oid) provides oxygen and nourishment to parts of the eye.
Eyelashes and eyebrows keep dust out of your eyes. Eyebrows also stop sweat from running into your eyes.
Tear glands inside your eyes make tears that wash over your eyes to keep them clean.
Caring for your eyes
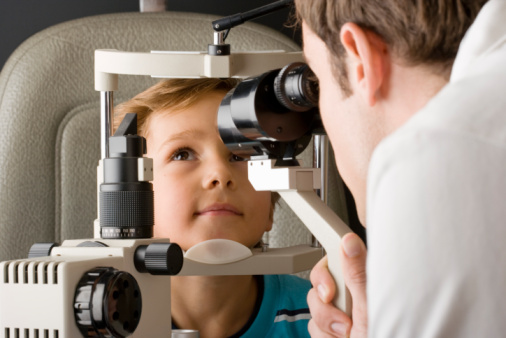
An eye doctor can examine your eyes to make sure they healthy and are working properly. © Getty Images
Sun glasses and other protective equipment are worn to protect the eyes from the sun's UV rays or during work activities when things might enter the eyes and hurt them. For example, mowing the grass or welding. When you are playing some sports such as cricket, wear a protective helmet. Goggles protect the eyes of skiers.
Rest your eyes from watching TV or using a computer screen. Take a break every now and then.
Looking directly at the sun is dangerous. Wear a hat to shade your eyes on sunny days.
Vision impairment
Glasses and contact lenses are worn by people whose eyes don't see properly.
An eye doctor or optician can test your eyes and correct common sight conditions such as short and long sightedness by making special lenses that help people see properly.
The boy is having his eyes tested by a doctor using an instrument called a phoropter, which will tell the doctor what spectacles the boy might need ©iStock
Severe vision impairment is blindness when someone cannot see at all, or very little.
Watch a video about vision impairment and how glasses help:
http://thekidshouldseethis.com/post/how-do-glasses-help-us-see-ted-ed
Read more about the eye:
http://www.ducksters.com/science/sight_and_the_eye.php
Read about visual impairment and blindness
https://kidshealth.org/en/kids/visual-impaired.html
https://www.perkins.org/10-little-known-facts-about-blindness/